# Associations
One of the most amazing things about Ruby on Rails is how easy it is to create Active Record associations (opens new window) between models. We try to keep the same simple approach in Avo too.
inverse_of as often as possible to your model's association attribute.
# Belongs to
field :user, as: :belongs_toCopied!
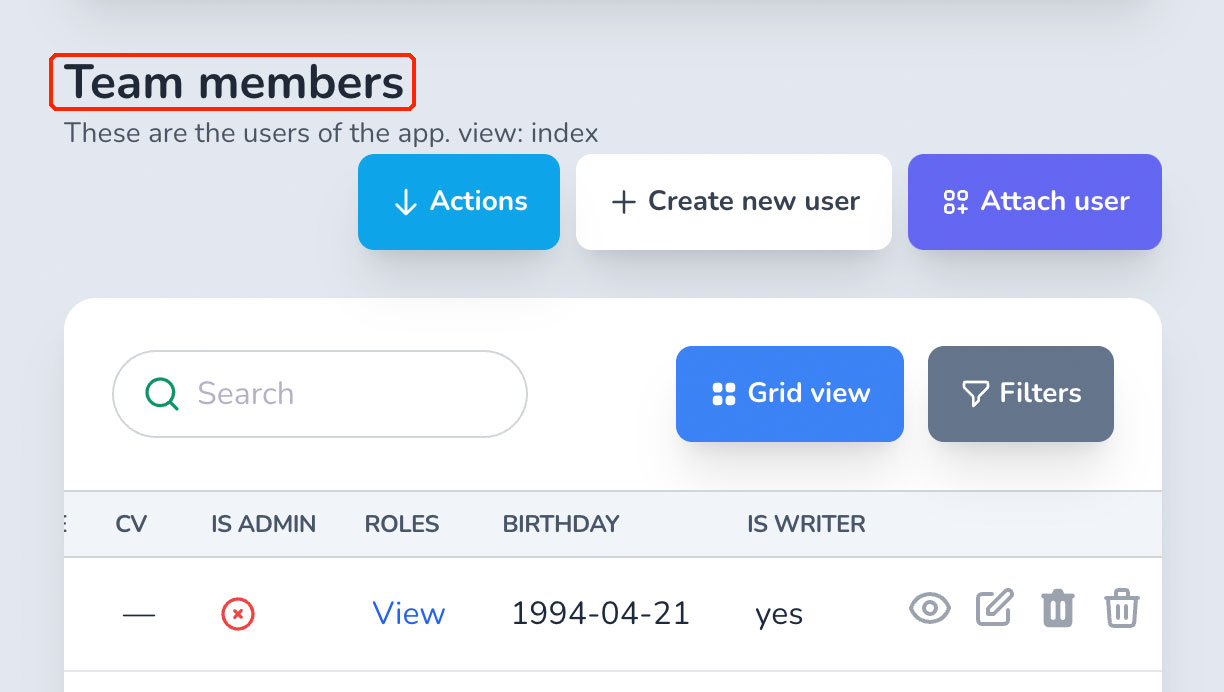
When you add a BelongsTo association to a model, you will see three different field types.
On the Index view, you'll see a column with the @title value of the associated model.

On the Show view, you'll see a link to the associated model.

On the Edit and Create views, you'll see a drop-down element with the available records. Here you may change the associated model.
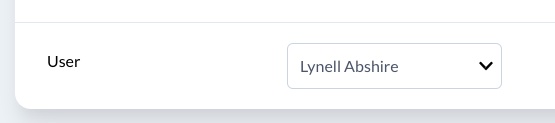
# Polymorphic belongs_to
To use a polymorphic relation you need to add the polymorphic_as and types properties.
class CommentResource < Avo::BaseResource self.title = :id field :id, as: :id field :body, as: :textarea field :excerpt, as: :text, show_on: :index, as_description: true do |model| ActionView::Base.full_sanitizer.sanitize(model.body).truncate 60 rescue "" end field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project] endCopied!
# Searchable belongs_to
Requires V 1.21 +
There might be the case that you have a lot of records for the parent resource, and a simple drop-down won't cut it. This is where you can use the searchable option to get a better search experience for that resource.
class CommentResource < Avo::BaseResource self.title = :id field :id, as: :id field :body, as: :textarea field :user, as: :belongs_to, searchable: true endCopied!
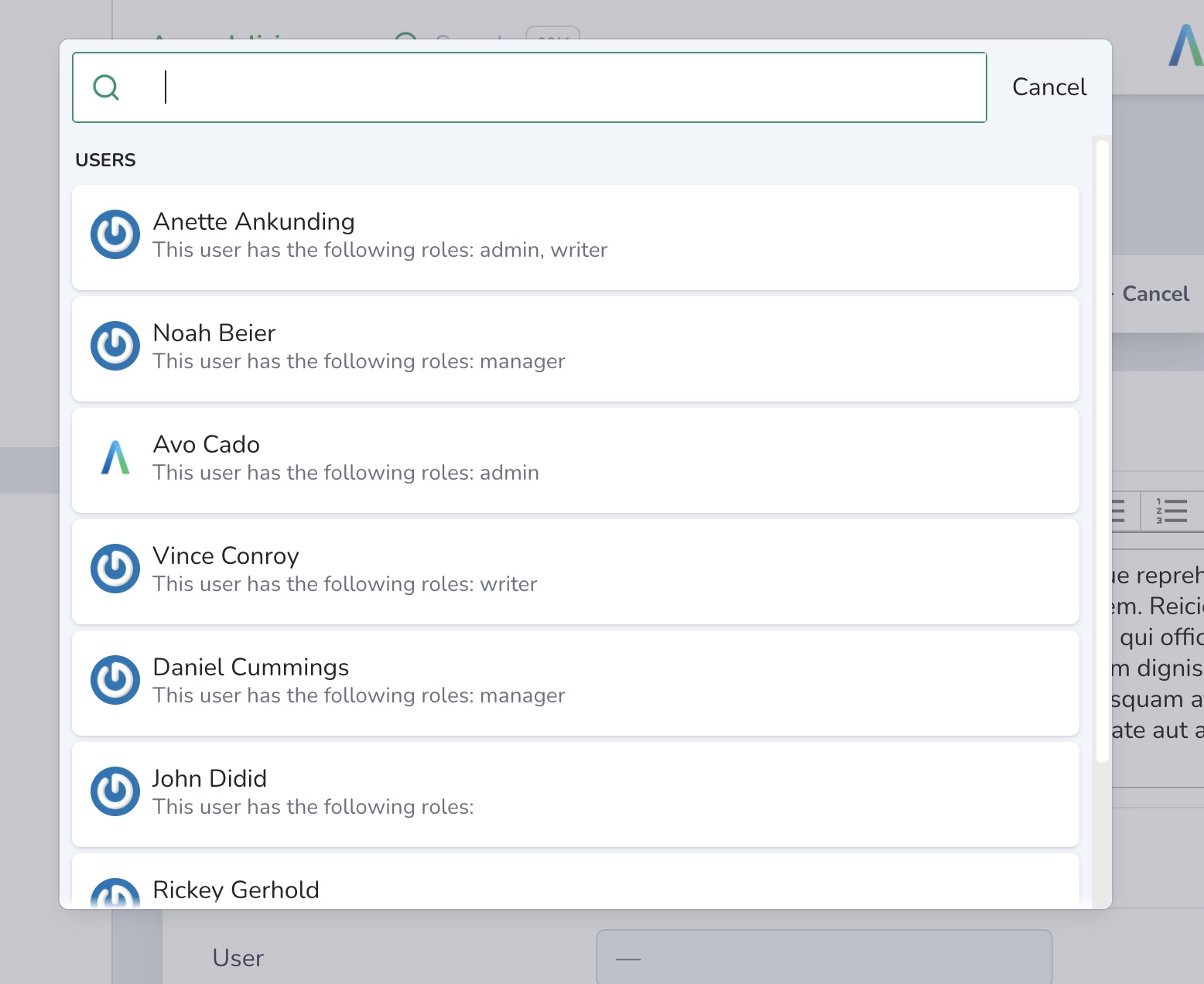
searchable works with polymorphic belongs_to associations too.
class CommentResource < Avo::BaseResource self.title = :id field :id, as: :id field :body, as: :textarea field :commentable, as: :belongs_to, polymorphic_as: :commentable, types: [::Post, ::Project], searchable: true endCopied!
Avo uses the search feature behind the scenes, so make sure the target resource has the search_query option configured.
Watch the video below to get an ideea on how it works.
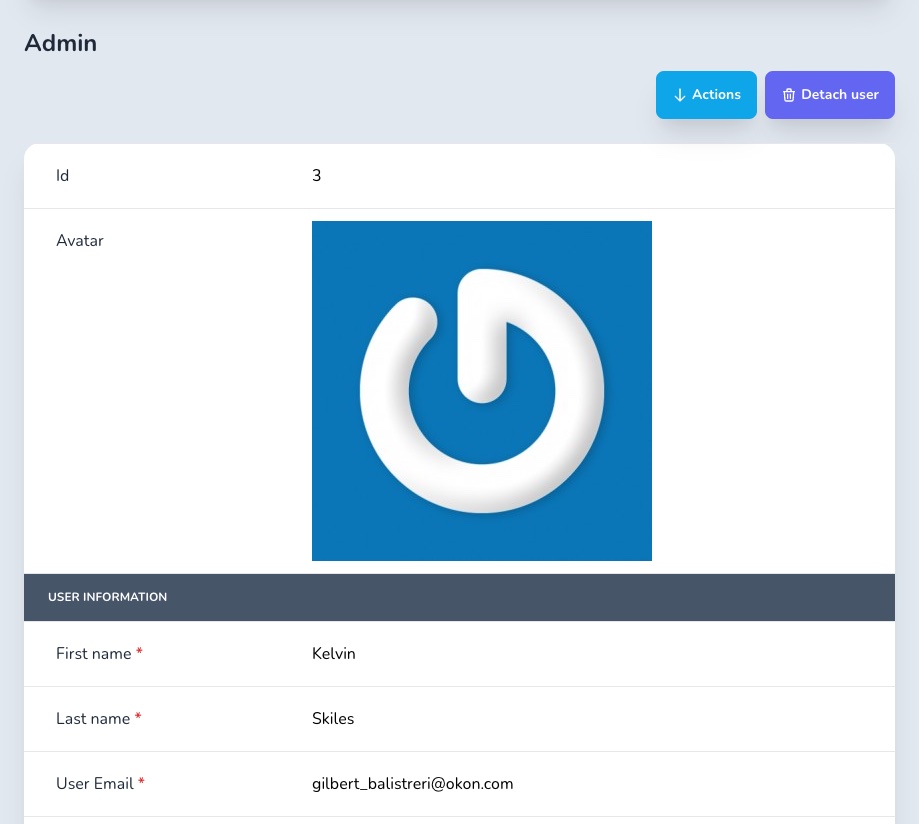
# Has One
The HasOne association shows the unfolded view of you HasOne association. It's like peaking on the Show view of that association. You also get the Attach/Detach button to easily switch records.
field :admin, as: :has_oneCopied!
# Has Many
The HasMany field is visible only on the Show page. Below the regular fields panel, you will see a new panel with the model's associated records.
field :projects, as: :has_manyCopied!
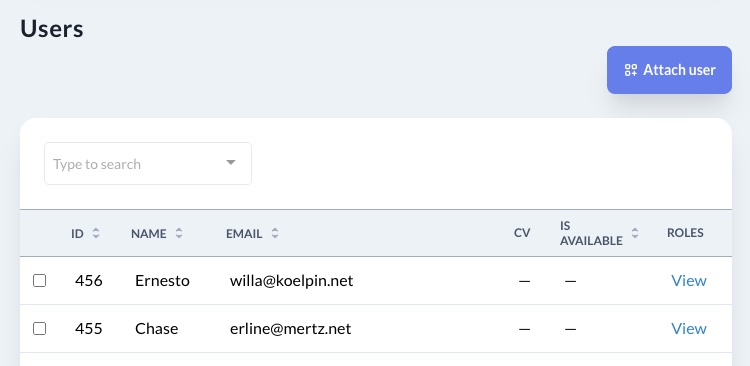
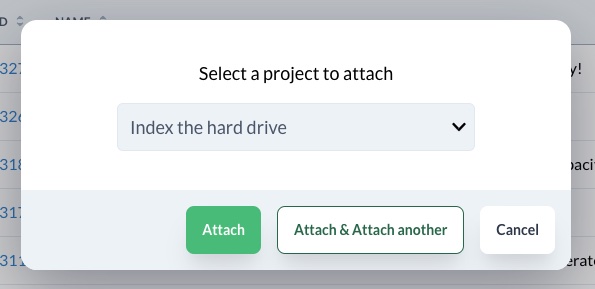
Here you may attach more records by clicking the "Attach" button.
In a similar fashion, you may detach a model using the detach button.
# Has many through
The HasMany association also supports the :through option.
field :members, as: :has_many, through: :membershipsCopied!
# Has And Belongs To Many
The HasAndBelongsToMany association works similarly to HasMany.
field :users, as: :has_and_belongs_to_manyCopied!
# Searchable has_many
Requires V 1.25 +
Similar to belongs_to, the has_many associations support the searchable option.
class CourseLink < Avo::BaseResource field :links, as: :has_many, searchable: true, placeholder: "Click to choose a link" endCopied!
Please note that the associated resource has to have the search option enabled.
# Single Table Inheritance (STI)
When you have models that share behavior and fields through with STI, Rails will cast the model as the final class no matter how you query it.
# app/models/user.rb class User < ApplicationRecord end # app/models/super_user.rb class SuperUser < User end # User.all.map(&:class) => [User, SuperUser]Copied!
For example, when you have two models, User and SuperUser with STI, when you call User.all Rails will return an instance of User and an instance of SuperUser. That confuses Avo in producing the proper resource of User. That's why when you deal with STI, the final resource SuperUserResource should receive the underlying model_class so Avo knows which model it represents.
class SuperUserResource < Avo::BaseResource self.title = :name self.includes = [] self.model_class = ::SuperUser field :id, as: :id field :name, as: :text endCopied!
# Add scopes to associations
When displaying associations, you might want to scope out some associated records. You can use the scope option to do that.
# app/models/comment.rb class Comment < ApplicationRecord belongs_to :user, optional: true scope :starts_with, -> (prefix) { where('LOWER(body) LIKE ?', "#{prefix}%") } end # app/models/user.rb class User < ApplicationRecord has_many :comments end # app/avo/resources/user_resource.rb class UserResource < Avo::BaseResource field :comments, as: :has_many, scope: -> { starts_with :a } endCopied!
Now, the comments query on the user Index page will have the starts_with scope attached.
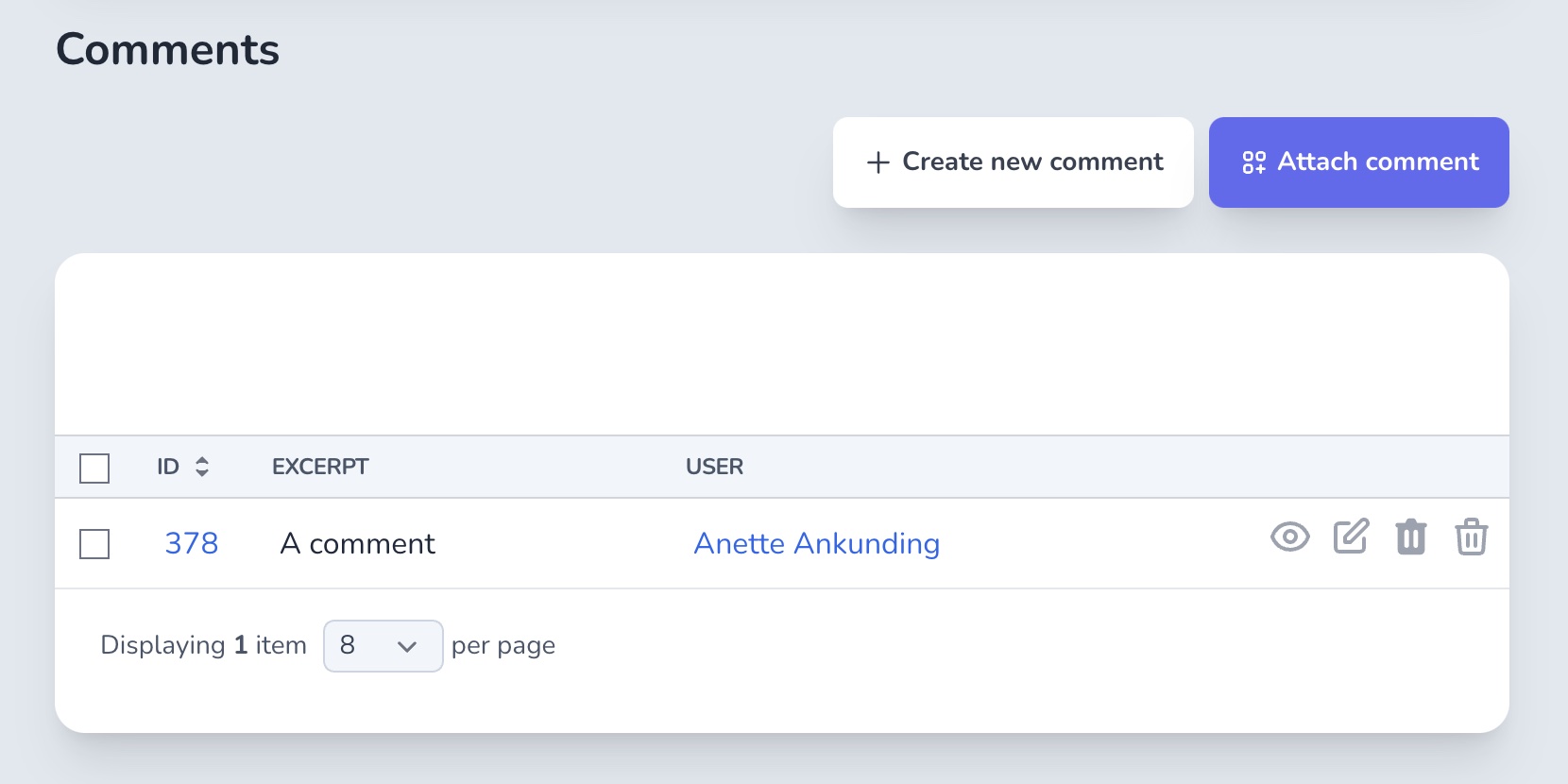
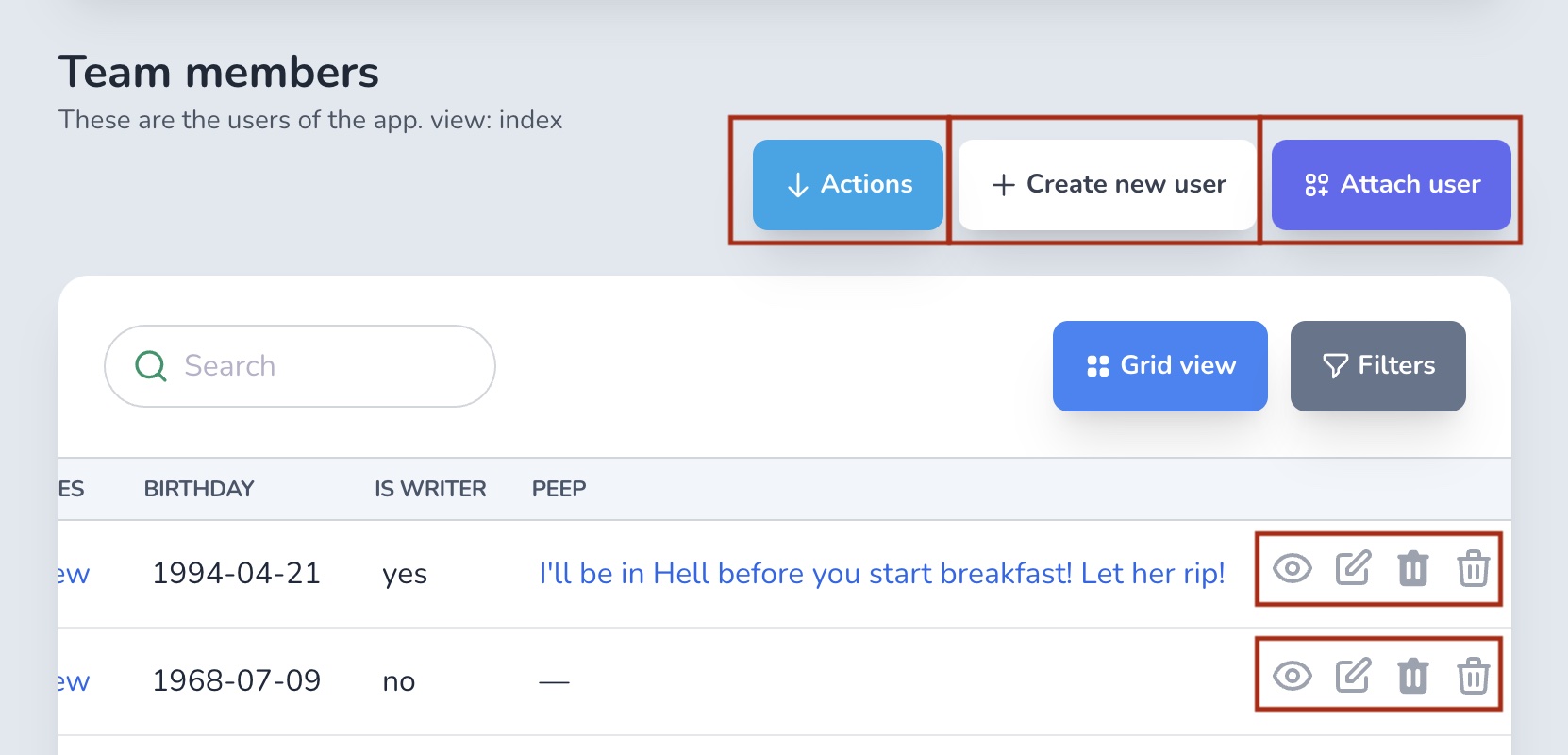
# Show/hide buttons
You will want to control the visibility of the attach/detach/create/destroy/actions buttons that are visible throughout your app. You can use the policy methods to do that.
Find out more on the authorization page.
# Add custom labels to the associations pages
You might want to change the name that appears on the association page. For example, if you're displaying a team_members associations, by default your users will see Team members as the title, but you'd like to show them Members.
You can customize that using fields localization.