# Fields
# Badge
The Badge field is used to display an easily recognizable status of a record in the database.

badge :stage, options: { info: [:discovery, :idea], success: :done, warning: 'on hold', danger: :cancelled } # The mapping of custom values to badge values.Copied!
By default, the badge field supports four values: info (blue), success (green), danger (red) and warning (yellow), having the possibility to override and or add values by providing options parameter.
The options parameter is a Hash the has the state as the key and your agreed values as value. The value param can be a symbol, string, or array of symbols or strings.
The Badge field is intended to be displayed only on Index and Show views. In order to update the value shown by badge field you need to use another field like Text or Select, in combination with hide_on: index and hide_on: show.
# Boolean
The Boolean field renders a input[type="checkbox"] and supports the following options.
boolean :is_published, name: 'Published', true_value: 'yes', false_value: 'no',Copied!
You might not use true/false or 1/0 to store the value in the database. By using true_value and false_value, you may declare different values for that database field like yes/no.
# Boolean Group

The BooleanGroup is used to update a Hash with string keys and boolean values in the database.
# Example boolean group hash { admin: true, manager: true, creator: true, }Copied!
boolean_group :roles, name: 'User roles'Copied!
# Code

The Code field generates a code editor using vue-codemirror (opens new window) package. This field is hidden on Index view.
code :custom_css, theme: 'dracula', language: 'css'Copied!
# Customize Theme
You can customize the theme of the Code field using the theme method. It defaults to material-darker, but you can choose from material-darker, eclipse, dracula. You can preview the themes here: codemirror-themes (opens new window).
# Customize Syntax Highlighting
You can customize the programming language highlighting of the Code field using the language method. It defaults to javascript but you can choose from css, dockerfile, htmlmixed, javascript, markdown, nginx, php, ruby, sass, shell, sql, vue or xml.
# Country
Country field generates a Select field on Edit view that includes all ISO 3166-1 (opens new window) countries. The value stored in the database is going to be the country code, and the value displayed in Avo is going to be the name of the country.
You can easily choose to display the name of the countries in Index and Show views by declaring display_name to true.
country :country, display_name: trueCopied!
# Currency
The Currency field generates a Number field that is automatically formatted using Vue Currency Input (opens new window) to look like a currency. You may use currency and locale to specify the sign and format of the currency field.
Be aware that currency defaults to USD, and locale defaults to en.
currency :salary, currency: 'EUR', locale: 'de-DE'Copied!
# Date
The Date field may be used to display date values.
The Edit** view of the picker is using flatpickr (opens new window). You may use the formatting tokens (opens new window) to format the Edit view element and the moment.js tokens (opens new window) to display the Index and Show views element.
You may also pass the first_day_of_week attribute to have that reflected on the generated calendar component. 1 is Monday (default), and 7 is Sunday.
date :birthday, first_day_of_week: 1, picker_format: 'F J Y', format: 'MMMM Do YYYY', placeholder: 'Feb 24th 1955', required: trueCopied!
If you'd like to show the time relative to the present (4 months ago, in 3 years, etc.) use the relative: true option.
date :valid_until, relative: trueCopied!
# DateTime
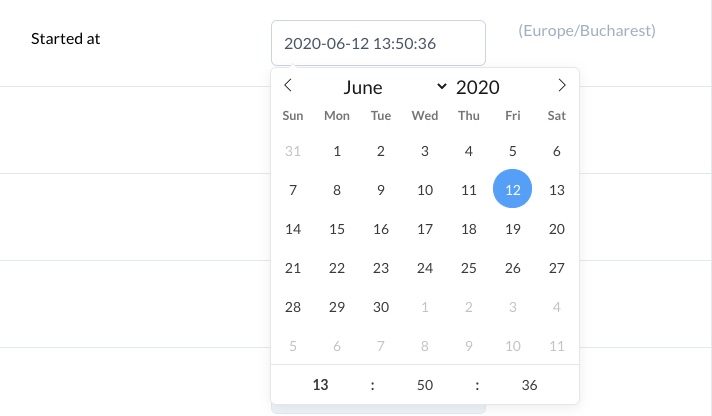
The DateTime field is similar to the Date field with two new attributes. time_24hr tells the component to use 24 hours format and timezone to tell it in what timezone to display the time.
datetime :created_at, name: 'User joined', first_day_of_week: 1, picker_format: 'Y-m-d', format: 'YYYY-MM-DD', time_24hr: true, timezone: 'PST'Copied!
# File
The File field may be used to attach files using Active Storage (opens new window). Avo will respect your application's Active Storage settings. You may use whichever supported disk services (opens new window).
file :avatar, is_image: trueCopied!
The is_image option renders the file as an image instead of rendering the file name.
# Files
The Files field is similar to File and enables you to upload multiple files at once using Active Storage (opens new window).
files :documentsCopied!
# Gravatar
The Gravatar field should be linked to an email field from the database, displaying the avatar image assigned to that email address in the Gravatar (opens new window) database. By default, it uses the email field, but if the email address is stored in another column, you can specify that column.
gravatar :email, rounded: false, size: 60, default_url: 'some image url'Copied!
On Index, by default, the image is rounded and has size of 40 px, but it can be changed by setting rounded to false and by specifying the size (in pixels) in field declaration.
On Show, the image is always squared and the size is responsive.
You can customize the image shown when gravatar is not found by changing the default_url attribute to a custom image URL.
# Heading

The Heading field is used to display a banner between fields, such as a separator for big lists or a header for different sections.
Heading is not assigned to any column in the database and only visible on Edit and Create views.
heading 'Address fields'Copied!
The as_html option will render it as HTML.
heading '<div class="underline text-gray-800 uppercase">Address fields</div>', as_html: trueCopied!
# Hidden
You might have a scenario where you need a value to update a model. You may use the Hidden field to add the field to the form a hidden input but not render it on the page.
hidden :group_idCopied!
# ID
The id field is used to show the record's id.
id :idCopied!
This is a good field to add as_link_to_resource option to make it a shortcut to the resource Show page.
# KeyValue

The KeyValue field allows you to edit flat key-value pairs stored in JSON format in the database.
key_value :metaCopied!
# Customizing the labels
You can easily customize the labels displayed in the UI by mentioning custom values in key_label, value_label, action_text, and delete_text properties when defining the field.
key_value :meta, # The database field ID key_label: 'Meta key', # Custom value for key header. Defaults to 'Key'. value_label: 'Meta value', # Custom value for value header. Defaults to 'Value'. action_text: 'New item', # Custom value for button to add a row. Defaults to 'Add'. delete_text: 'Remove item' # Custom value for button to delete a row.. Defaults to 'Delete'.Copied!
# Enforce restrictions
You can enforce some restrictions by removing the ability to edit the field's key, by setting disable_editing_keys to true. Be aware that this option will also disable adding rows as well. You can separately remove the ability to add a new row by setting disable_adding_rows to true. Deletion of rows can be enforced by setting disable_deleting_rows to true.
key_value :meta, # The database field ID disable_editing_keys: false, # Option to disable the ability to edit keys. Implies disabling to add rows. Defaults to false. disable_adding_rows: false, # Option to disable the ability to add rows. Defaults to false. disable_deleting_rows: false # Option to disable the ability to delete rows. Defaults to false.Copied!
KeyValue is hidden on Index view.
# Markdown
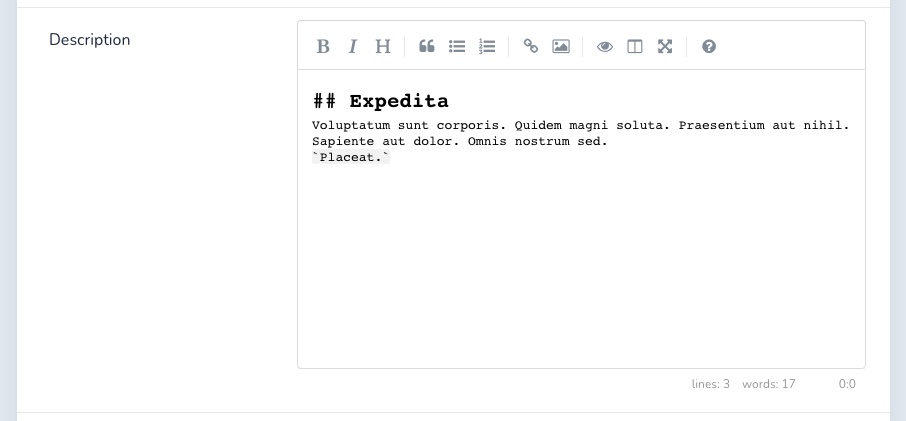
The Markdown field renders a Markdown Editor (opens new window) and is associated to a text or textarea column in the database.
Markdown field converts text within the editor in raw Markdown text and stores it back to database.
Markdown field is hidden from Index view. By default, the Markdown field is not directly shown to the user on the Show view, instead being hidden under a
'Show Content' link, that triggers the visibility of the content. You can set Markdown to always display the content by setting always_show to true.
markdown :description, always_show: trueCopied!
# Number
The Number field renders a input[type="number"] element and has the regular min, max, and step options.
number :age, min: 0, max: 120, step: 5Copied!
# Password
The Password field renders a input[type="password"] element for that field.
Password field is by default enforced to be shown only on :forms (:create and :edit). Because of security reasons, this type of field allows
only a few additional options for view visibility: only_on, hide_on methods and :create, :edit options for each method.
password :password placeholder: 'secret',Copied!
# Select
The Select field renders a select field.
select :type, options: { large: 'Large container', medium: 'Medium container', small: 'Tiny container' }, display_with_value: true, placeholder: 'Choose the size of the container.'Copied!
You may add options using the options option, which is a Hash with the id (database value) as the key and the label as value.
On Index, Show and Edit views you may want to display the values and not the labels of the options. You may change that by setting display_value to true.
The Select field also supports Active Record hash enums (opens new window). For that to work you only need to remove options and add enum instead.
class Project < ApplicationRecord enum type: { 'Large container': 'large', 'Medium container': 'medium', 'Tiny container': 'small' } end select :type, enum: ::Project.types display_with_value: true, placeholder: 'Choose the size of the container.'Copied!
This tells Avo to treat the value and the options a bit different because of the way Rails casts the attribute with the value from the enum.
# Status
The Status field is used to visually display the status of a column, supporting the following options:
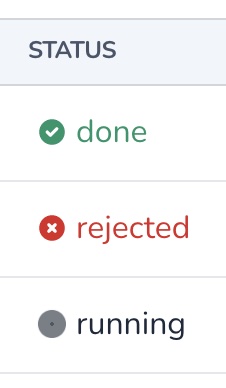
status :progress, failed_when: ['closed', 'rejected', 'failed'], loading_when: ['loading', 'running', 'waiting', 'in progress']Copied!
You may customize the failed and loading states by using failed_when and loading_when. failed_when defaults to failed, while loading_when defaults to both waiting and running.
# Text
The Text field renders a regular text input.
text :titleCopied!
You may customize it with as many options as you need.
text :title, # The database field ID name: 'Post title', # The name you want displayed required: true, # Display it as required readonly: true, # Display it disabled placeholder: 'My shiny new post', # Update the placeholder text format_using: -> (value) { value.truncate 3 } # Format the outputCopied!
# Textarea
The Textarea field renders a textarea element and takes has the rows option that controls how many rows it should render.
textarea :body, rows: 5Copied!
# Trix
The Trix field renders a WYSIWYG Trix Editor (opens new window) and is associated to a text or textarea column in the database.
Trix field converts text within the editor in HTML and stores it back to database.
Trix field is hidden from Index view. By default, the Trix field is not directly shown to the user on the Show view, instead being hidden under a
'Show Content' link, that triggers the visibility of the content. You can set Trix to always display the content by setting always_show to true.
trix :body, always_show: trueCopied!
